
Translation Agency | Email US | Translation Resources | Translation Jobs | Translation Agencies
World Languages | Translation Tips | Translation Services
Translations of
Encyclopedia by Czech and Slovak to English translator

Translation Agency |
Email US |
Translation
Resources | Translation Jobs | Translation Agencies
World Languages | Translation Tips | Translation Services
According to the plate tectonics theory, the upper part of the earth's mantle,
lithosphere, is not an individual layer, but consists of a number of rigid plates floating on the athenosphere. The question is, why do these plates move?Most likely, the answer to this question may be found in the earth's core. The earth's mantle underneath the lithosphere is hot and malleable. The
energy required for this heat is related to the radioactive processes in the core of the earth. The heat rises slowly upwards. The convective movement originates because the rigid, malleable material is being heating on the lower side, while on the upper side it is cooling down.We all know, that warm material expands, reaches lower
density, and rises, while cooled mass becomes denser, heavier, and descends. We can compare this process to heating water in a pot. The bubbles in the boiling water allow it to rise. We see it in the form of the escaping water vapour. Alternatively, we can look at the earth as a pot of soup, with a top layer of thin crust. If we move the pot so that half of it is off the burner, we can create a strong convection current within the pot, the heat of the burner rising up on one side, cooling at the surface, and then moving down the other side of the pot, to create a large convection current. Relative to the size of the earth, it's crust is quite thin, and hence susceptible to movement by the convection currents within the earth, much like the top crusty layer of the pot of soup moves as a result of the convection current within the pot. The shifting of the earth's thin crust results in the movement of entire continents. <add some pics>
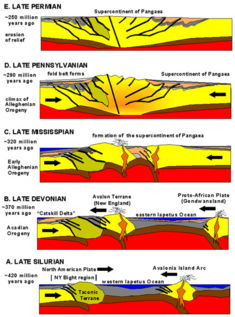 |
In the case of the earth's crust movement it works as follows: where the hot material from the earth's interior upwards and spills over on the side, the plates are pulled in the opposite direction and separated from other plates, as may be observed in the case of mid-ocean plates. The molten magma rises and spreads on the sides. When it cools down, it forms the lithosphere.On other plate boundaries in the subductive regions, cold material descends and pulls the plate downwards. The descending material consists of the cold lithosphere. These movements are not a fast, continuous phenomenon. They are barely measurable changes ranging from a few millimetres to a few centimetres. These movements, occurring in different places and at different times, certainly reach different speeds. Some geologists believe that the convective flow occurs only in the region of the earth's mantle. Although the geologists do not agree on individual issues, they are all in agreement in that the convective flow from the interior to the surface, during which the seafloor spreading occurs, is an important process allowing the earth to cool throughout its geological evolution up to this time. |
Compared to the much higher energy we receive from the sun, which is 5000 times higher, the thermal energy of the earth's core is very low. However, it is strong enough to move the lithospheric plates, form
mountain ranges, or produce earthquakes. The geologists estimate the temperature distribution based only on the study of volcanoes, seismic waves, and laboratory work. According to their calculations, the temperature in the earth's core reaches 4000 to 5000 degrees Celsius.Translating Spanish Hungarian Translations Hungarian Spanish Translating Norwegian Italian Translations Italian Norwegian Translating Czech
Translation Agency |
Email US |
Translation
Resources | Translation Jobs
Translation Agencies | World Languages | Translation Tips | Translation Services

Copyright © KENAX, by Karel Kosman - All Rights Reserved Worldwide.